Even in 2026, cash registers remain a part of many retail environments—but how they’re used has changed significantly. Today’s cash registers are often paired with digital POS systems, barcode scanners, receipt printers, and cloud-based software, making them far more powerful than the traditional tills of the past.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to use a cash register in 2026, from basic transactions and cash handling to integrating with modern POS features. Whether you’re running a small shop, training new staff, or transitioning from a traditional register to a POS system, this article will help you understand best practices for efficient, accurate checkout in today’s retail landscape.
What Is a Cash Register in 2026?
A cash register in 2026 is no longer just a mechanical drawer for storing cash. Modern cash registers are typically electronic or hybrid systems, often connected to tablets, POS software, barcode scanners, and receipt printers. Many models now support card payments, contactless transactions, and even cloud-based reporting.
These systems are commonly used by:
- Small retail stores
- Convenience shops
- Cafés and food stalls
- Pop-up shops and temporary retail setups
Basic Components of a Modern Cash Register
Before using a cash register, it’s important to understand its core components:
- Display screen for transaction details
- Keypad or touchscreen for input
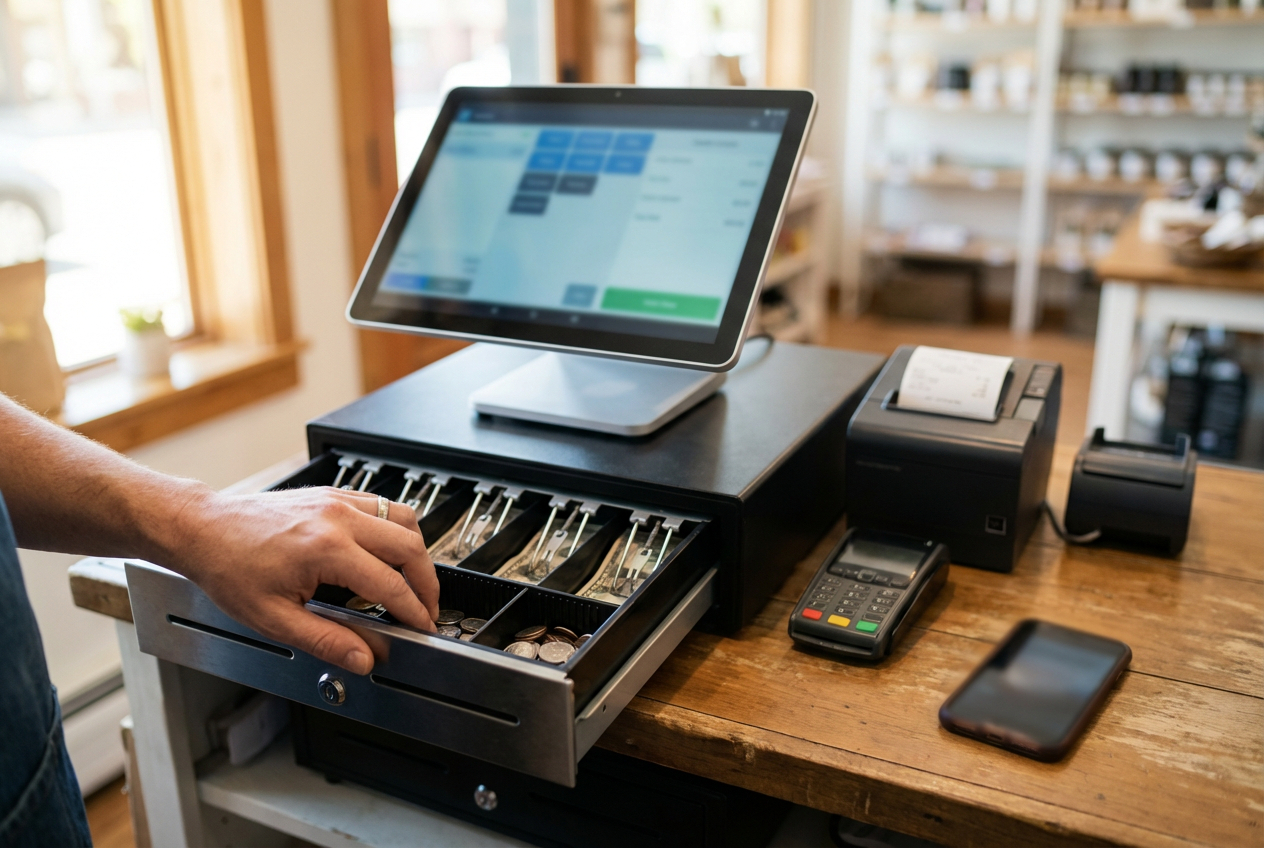
- Cash drawer for storing cash
- Receipt printer for transaction records
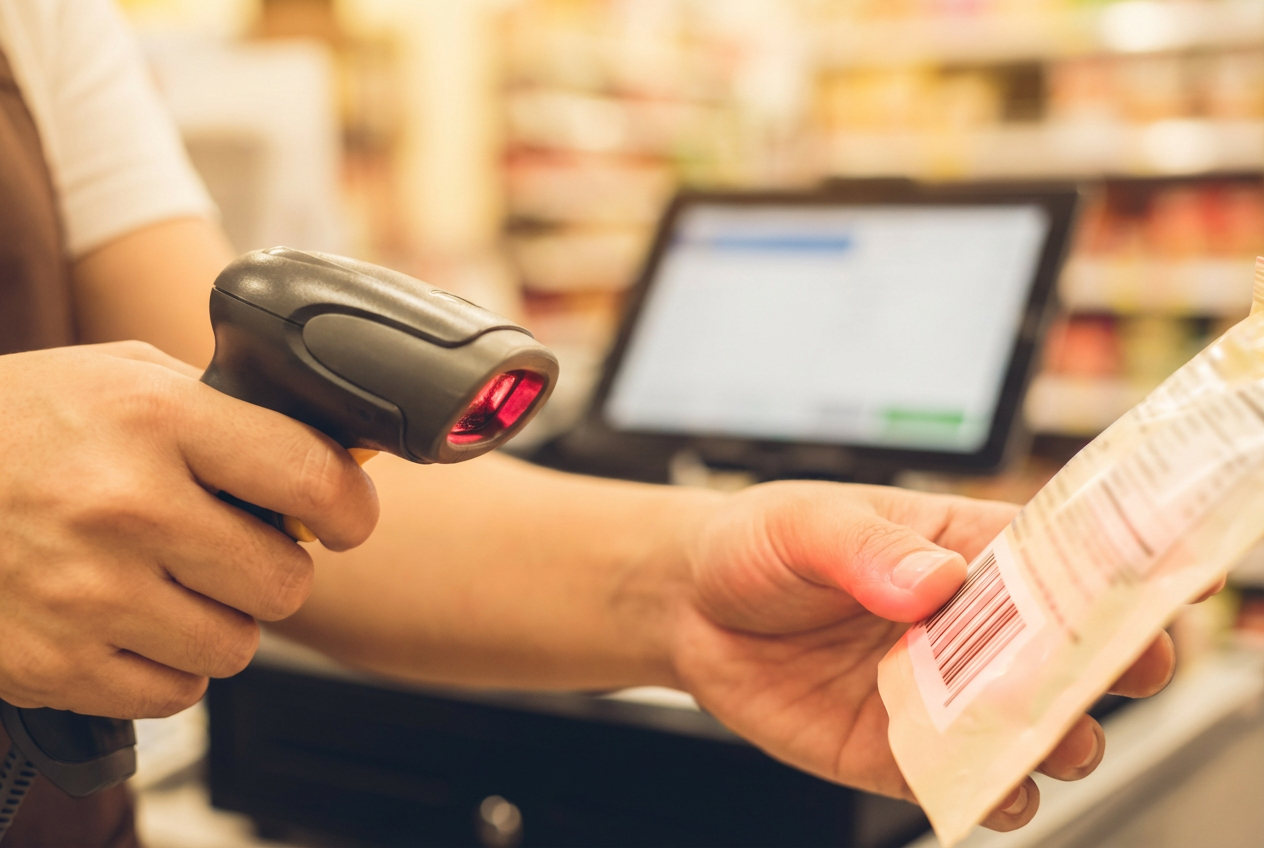
- Barcode scanner (optional but common)
- Payment terminal for card and contactless payments
Many modern setups combine these components into a single system or connect them through POS software.
Types of cash registers
Different businesses require different types of cash registers; here’s a look at the options that could suit your specific needs.
Electronic cash register (ECR)
Electronic cash registers are the traditional backbone of retail checkout points. Equipped with a cash drawer and an input method, such as a keypad or touchscreen, ECRs are designed for durability and ease of use. Most come with integrated receipt printers and barcode scanners, and they can operate via a direct power source or batteries.
POS cash register
►►► Optimal solution set for businesses: Multi store POS, Next-gen POS, Inventory Management Software (MSI), Self Service, Automation, Backorders

The advent of Point-of-Sale (POS) systems has revolutionized how to use a cash register. These versatile systems offer expanded capabilities including in-depth customization to fit specific business needs. POS registers typically come with scanners and utilize advanced software to conduct crucial business analytics, manage inventory, and evaluate product performance, enhancing the business’s operational efficiency.
Mobile cash register
Mobile cash registers bring portability to the sales process. These systems work similarly to traditional registers but are housed in mobile devices like tablets. They are cost-effective and can be activated quickly to serve as additional checkout points, providing flexibility to manage customer flow, particularly during peak hours.
Cloud-based cash register
The latest innovation in cash register technology is the cloud-based system. These systems harness the power of cloud computing to synchronize operations across multiple devices, be they computers or tablets. A cloud-based cash register is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing for real-time monitoring and updates from any location, giving businesses unprecedented agility and control over their sales data.
Read more: What is a cash float
Functions of a cash register
Cash registers serve as the hub for transaction processing in retail settings. Understanding their capabilities is essential for efficient business operations.
Basic functions
- Processing a sale: The primary role of a cash register is to facilitate the sale process. It involves scanning items, totaling the cost, accepting payment, and issuing receipts.
- Entering discounts: Cash registers allow the input of discount codes or manually applied price reductions during a sale, ensuring promotions and special offers are reflected in the final price.
- Managing returns and refunds: They efficiently handle transaction reversals, allowing customers to return goods and issue refunds as necessary.
- Voiding transactions: In the event of an error, cash registers can void transactions before finalizing them, ensuring accuracy in sales records and financial reports.
Advanced features
- Inventory tracking capabilities: Modern cash registers can be synced with inventory management systems to track stock levels in real-time, aiding in reorder processes and loss prevention.
- Integration with other business systems: Many cash registers can integrate seamlessly with CRM, accounting software, and other business management tools to centralize operations and data insights.
- Customizable reports and analytics: With advanced systems, users can generate detailed reports on sales trends, peak business hours, customer preferences, and more, providing valuable analytics to inform business strategy.
How To Use a Cash Register: Step-by-Step
To use a cash register in 2026, power it on, log in, and scan or manually enter items, then select the payment method (cash, card, etc.) and process the payment, which opens the cash drawer for cash transactions. After payment, the system prints a detailed receipt for the customer. At the end of the day, generate a report to reconcile sales and manage the cash drawer by balancing it with the recorded totals.
1. Start the Register and Log In
Power on the cash register and log in using your assigned user code or key. This allows managers to track sales by employee and maintain accountability.
2. Enter or Scan Products
- Manually enter item prices using the keypad, or
- Scan product barcodes using a connected barcode scanner
The register will automatically calculate totals, taxes, and discounts if configured.
3. Apply Discounts or Promotions
If applicable, select discount buttons or promotional codes. Many registers allow preset discounts for sales, loyalty programs, or special offers.
4. Accept Payment
Choose the payment method:
- Cash
- Credit or debit card
- Contactless payment
- Mobile wallet
For cash payments, enter the amount received, and the register will calculate the correct change.
5. Complete the Sale
Once payment is approved:
- The cash drawer opens automatically
- A receipt is printed or sent digitally
- The transaction is recorded in the system
6. Issue Receipts
Receipts can be:
- Printed
- Emailed
- Sent via SMS
Digital receipts are increasingly popular in 2026 for sustainability and customer convenience.
Modern Features to Use in 2026
Today’s cash registers often include advanced capabilities:
Inventory Tracking: Sales automatically update inventory levels, helping prevent stockouts and overselling.
Sales Reports: Daily, weekly, or monthly reports provide insights into:
- Top-selling items
- Peak sales hours
- Staff performance
Customer Management: Some systems store customer details for loyalty programs, discounts, and repeat purchases.
Offline Mode: If the internet goes down, transactions can still be processed and synced later.
Cash Register vs POS System in 2026
While cash registers are still useful, many businesses are transitioning to full POS systems.
Cash Register Advantages
- Lower upfront cost
- Simple operation
- Suitable for small or low-volume stores
POS System Advantages
- Advanced inventory management
- Omnichannel selling (online + in-store)
- Real-time analytics
- Better scalability
If your business is growing or selling across multiple channels, upgrading to a POS system may be the smarter long-term choice.
Conclusion
Using a cash register in 2026 is about more than handling cash—it’s about combining simplicity with modern technology. Today’s electronic and hybrid cash registers offer faster checkout, better tracking, and integration with digital payments, making them suitable for many small and mid-sized businesses.
However, as retail continues to evolve, businesses should regularly evaluate whether a traditional cash register still meets their needs or if a full POS system would deliver greater efficiency and growth potential. By understanding how to properly use and manage a cash register, you can ensure smooth daily operations while preparing your business for the future.
For those looking to embrace the full potential of modern retail technology, ConnectPOS offers a suite of solutions tailored to meet these needs. Our systems are designed with the user in mind, ensuring an intuitive experience that complements your business’s best practices. Get in touch to discover how our POS systems can transform your sales process
►►► Optimal solution set for businesses: Shopify POS, Magento POS, BigCommerce POS, WooCommerce POS, NetSuite POS, E-Commerce POS